Introduction
This tutorial guides you through various strategies to optimize CI/CD workflows in Semaphore, though many of these practices are also applicable to other CI/CD tools.
Our focus here is on techniques that minimize resource consumption and make your workflows run faster. By the end of this guide, you will understand how to improve feedback loops and project performance through dependency caching, fail-fast strategies, auto-cancel policies, and conditional job executions.
Prerequisites
Before starting, you should have:
- An active Semaphore account.
- A foundational understanding of CI/CD principles.
Reducing Build Times with Dependency Caching
Challenge: A considerable portion of build time in CI/CD pipelines is often consumed by reinstalling dependencies that rarely change, which delays feedback and uses resources unnecessarily.
Solution: Adding Dependency Caching
Two commands, cache store and cache restore can be used to manage dependency caching.
Example: Implementing Caching in a React Project
# semaphore.yml snippet for caching npm dependencies
blocks:
- name: "Install dependencies"
task:
prologue:
commands:
- checkout
- cache restore $SEMAPHORE_GIT_BRANCH-$(checksum package.json), $SEMAPHORE_GIT_BRANCH, cache-master
jobs:
- name: npm install
commands:
- npm install
- cache store $SEMAPHORE_GIT_BRANCH-$(checksum package.json) node_modules
This configuration checks for changes in package.json and uses the cache when there are no updates, reducing unnecessary installations.
📚 Learn more about caching and its strategies in the documentation.
Using Fail-Fast Strategies to Conserve Resources
Challenge: Continued execution of jobs after a failure in one job can lead to wasted computational resources.
Solution: Implementing Fail-Fast
Semaphore includes options to immediately stop executing other jobs when a failure is detected, which helps to preserve resources.
Example: Implementing Fail-Fast in your Workflow
# semaphore.yml snippet for fail-fast strategy
version: v1.0
name: Example Semaphore CI pipeline
agent:
machine:
type: e1-standard-2
os_image: ubuntu2204
fail_fast:
stop:
when: "any"
This configuration cancels all pending jobs if any job fails.
We can also configure this by using the Workflow Builder:
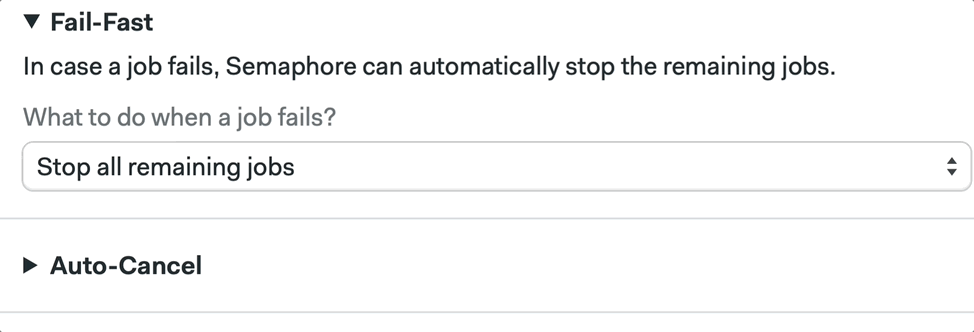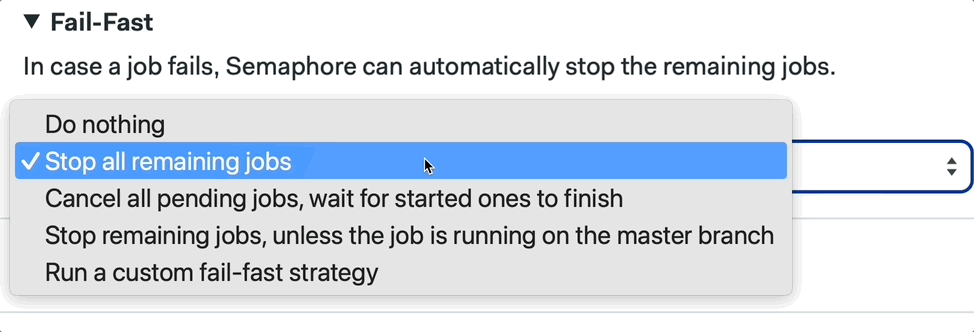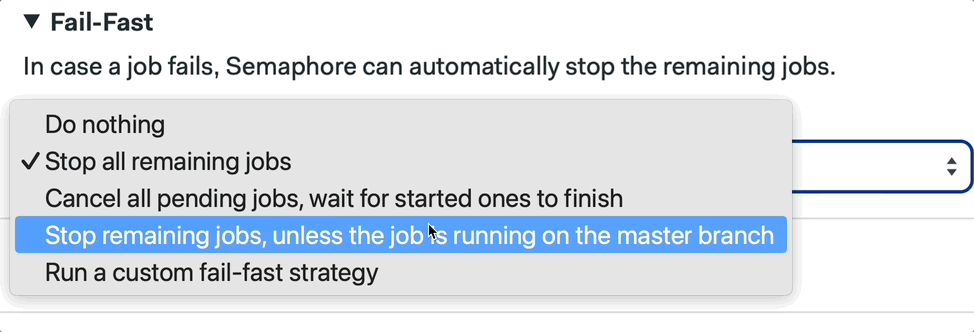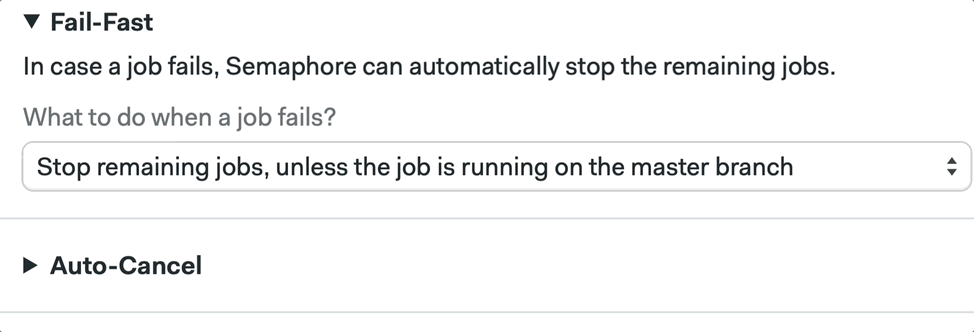
📚 Learn more about fail fast and its strategies in the documentation.
Canceling Redundant Builds
Challenge: Multiple pipelines running for several commits on the same branch can lead to redundant builds.
Solution: Setting Up Auto-Cancel
The auto-cancel feature helps manage resources by canceling redundant pipeline executions.
Example: Auto Cancel all new commits on existing branch
# semaphore.yml snippet for auto-cancel policy
auto_cancel:
queued:
when: "branch_has_new_commit"This setting cancels all queued jobs on a branch when a new commit is pushed.
We can also configure this by clicking on the pipeline and going into the Auto-Cancel tab using the Workflow Builder:
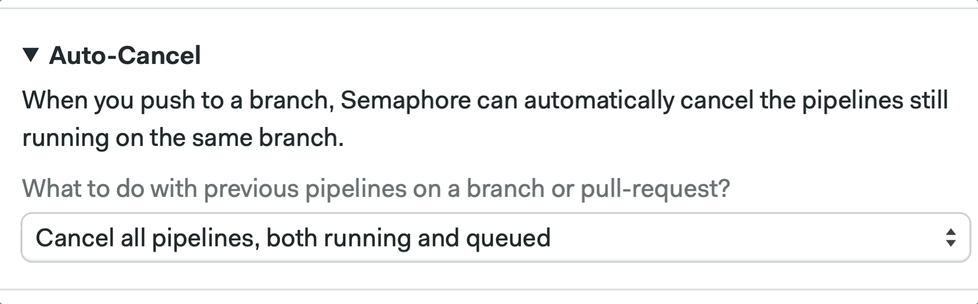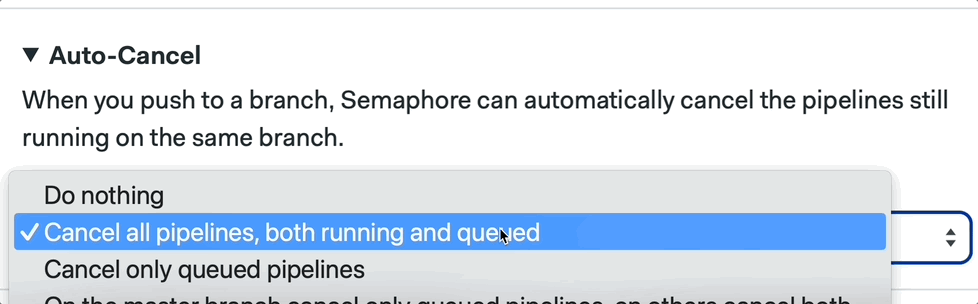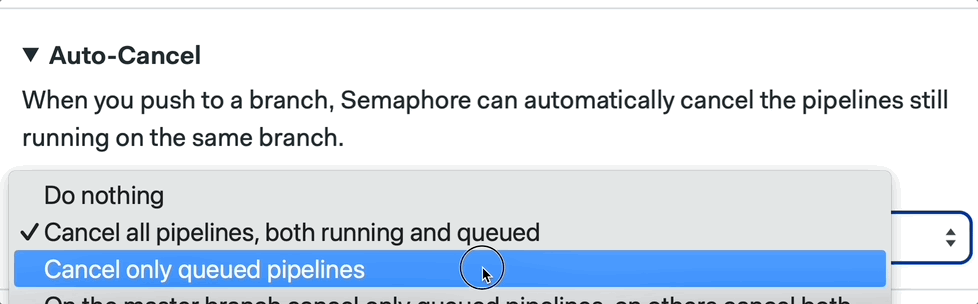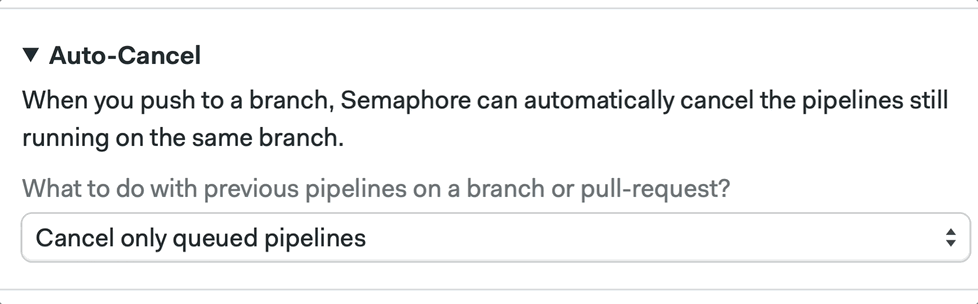
📚 Learn more about auto cancel and its strategies in the documentation.
Optimizing Execution with Conditional Job Runs
Challenge: Executing jobs when no relevant code changes have occurred increases build times and resource use.
Solution: Using Conditional Job Execution
The change_in function allows jobs to run only when specific changes are detected in the codebase.
Example: Run Tests Block only if folder tests has changed
# semaphore.yml snippet for conditional job execution
blocks:
- name: "Run Tests"
run:
when: "change_in('/tests/')"This configuration runs the test block only if there are changes in the tests directory.
We can also configure this using the Workflow Builder, by selecting a block and defining the Skip/Run conditions:
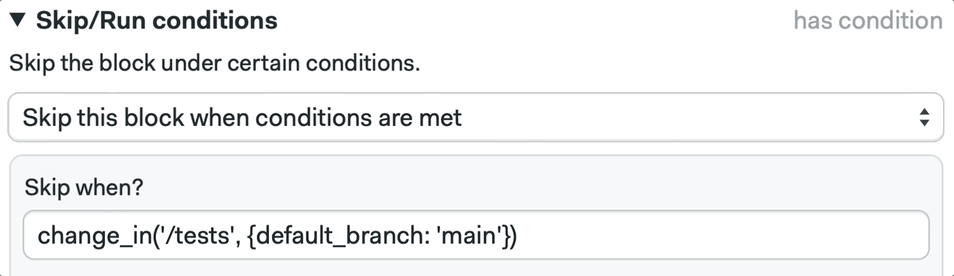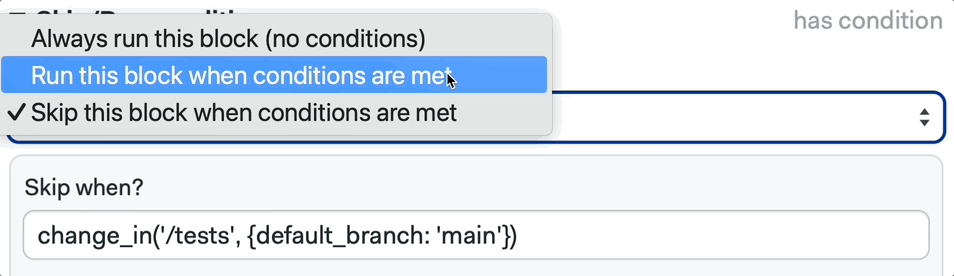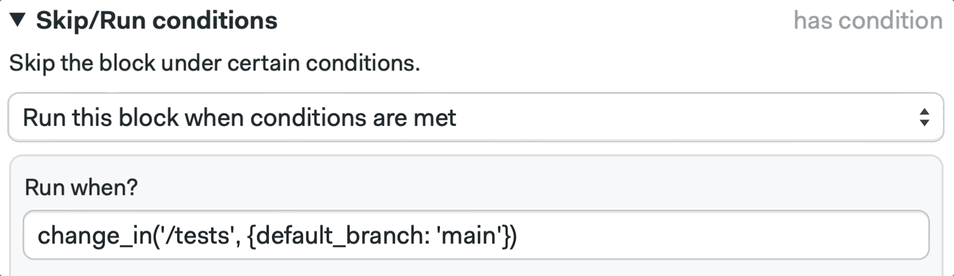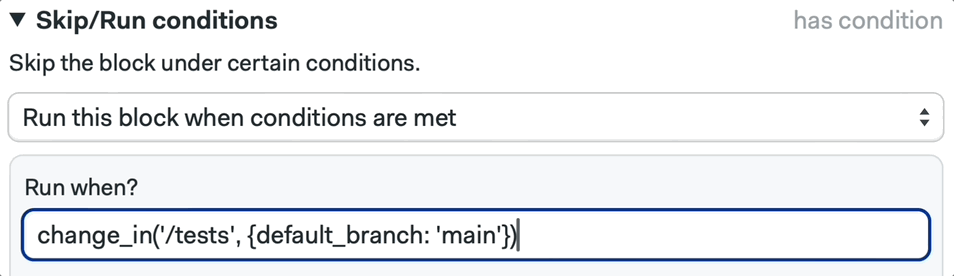
📚 Learn more about the change_in command and its strategies in the documentation.
🎥 Video
Check out the accompanying video to see these optimizations in action 💪
Conclusion
By implementing the strategies detailed in this guide, you can decrease build times and operational costs in Semaphore. The techniques provided in this guide can be adapted to other CI/CD platforms as well.
